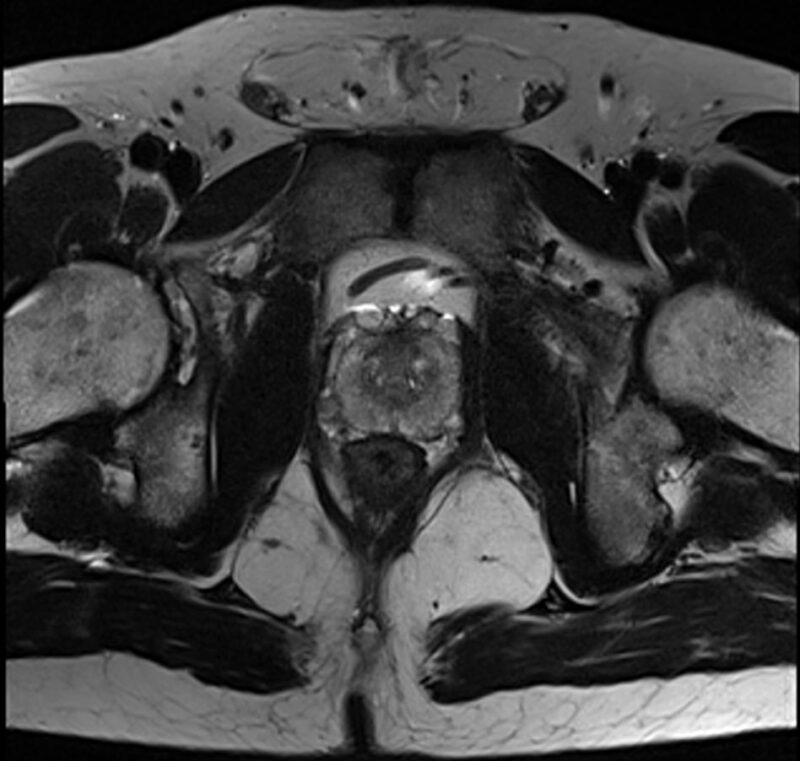
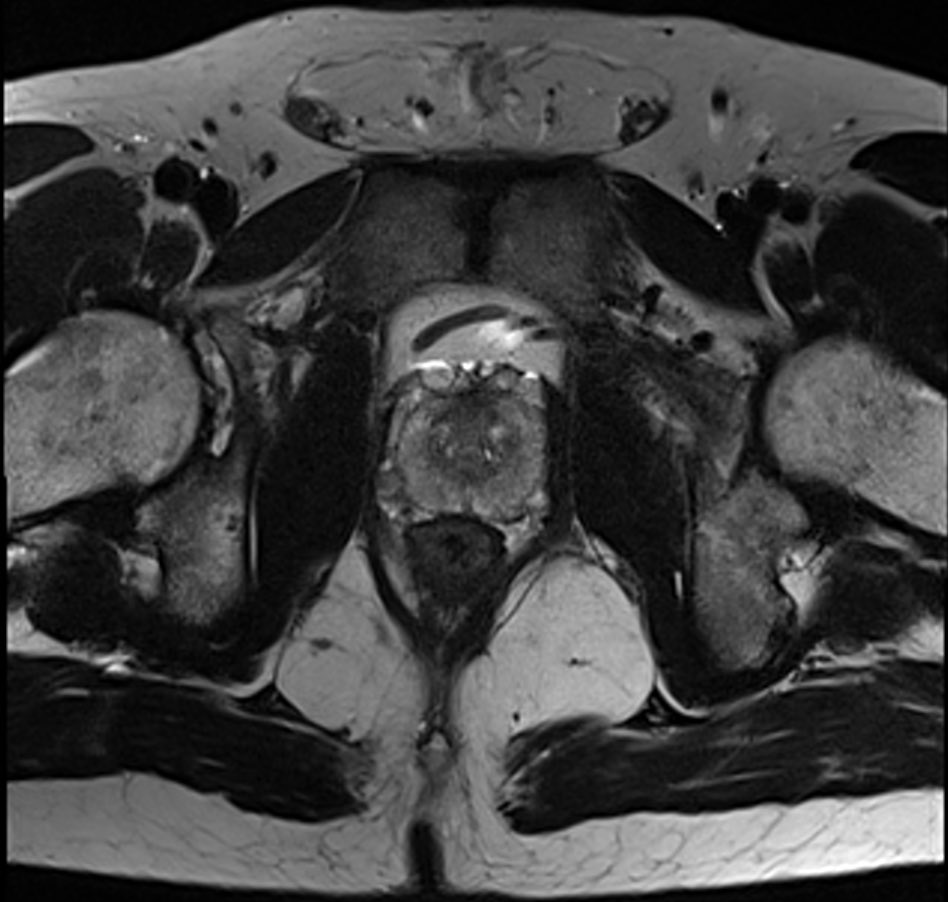
Using biparametric (bp) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to screen for prostate cancer identified twice as many clinically significant cancers as standard prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests. Moreover, the UK study, reported in JAMA Oncology (11 February), found bpMRI improved detection of prostate cancers without leading to unnecessary biopsy or over diagnosis. In contrast, ultrasonography, was found unlikely to improve screening performance.
“The encouraging results of this research study bring a mass screening programme for prostate cancer, equivalent to mammogram testing for women, a step closer,” says David Eldred-Evans, the corresponding author. The study, he adds, represents the first time a new fast approach to MRI, known as bpMRI, has been used in a general population to screen for prostate cancer.
Although it is unclear whether the benefits of PSA screening for prostate cancer outweigh the risks of false positive results and over diagnosis of insignificant prostate cancers there has not been a viable alternative approach for screening. The reason is that standard MRI has not been considered of sufficient sensitivity to provide detailed enough images of the prostate to screen for cancer. The development of multiparametric MRI (mpMRI), with additional assessments of water molecule motion (water diffusion) and blood flow (perfusion imaging), delivered greater image clarity. However, mpMRI examinations have the disadvantage of being lengthy (taking over 30 minutes), and requiring administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents, presenting problems of the inconvenience of intravenous cannulation and potential risks for adverse effects (including nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium deposition in the brain). “While mpMRI is used to assess men already found to have raised PSA, it wouldn’t be feasible to use as a screening test due to the time, cost and risks from intravenous contrast,” explains Eldred-Evans. In consequence, mpMRI is not considered suitable for screening and instead used when the clinical suspicion for prostate cancer is high following high PSA levels.
To address these issues, bpMRI, also known as short MRI, has been developed to speed up the process (it lasts just five to 10 minutes) by focusing solely on the immediate prostate area and by removing the need for contrast agents. “Our version of bpMRI just provides a snapshot that is focused on the prostate. If we do detect cancer we can then follow-up with more detailed scans looking at areas beyond that prostate,” explains Eldred-Evans.
In the Imperial Prostate 1 Prostate Cancer Screening Trial (IP1-PROSTAGRAM) study, Eldred-Evans, from Imperial College, London, and colleagues, set out to determine the performance of PSA, bpMRI and ultrasonography. Between October 2018 and May 2019, 408 men, aged 50 to 69 years, from seven primary care practices were screened using each of the three methods. If results of any of the tests were positive, subjects underwent a systematic 12-core biopsy of the entire gland, with additional targeted biopsy at the sites of any imaging abnormalities. Rates of screen positives requiring biopsy and of clinically significant cancer detection, defined as Gleason scores of 3+4 or greater, were then compared.
Results showed that the proportion of men with positive tests was 9.9% for PSA versus 17.7% for bpMRI (P<.001), and 23.7% for ultrasonography (P<.001). The results showed that the PSA test (≥3ng/mL) detected seven clinically significant cancers, an MRI score of 3 to 5 detected 14 cancers, an MRI score of 4 to 5 detected 11 cancers, an ultrasonography score of 3 to 5 detected nine cancers, and an ultrasonography score of 4 to 5 four cancers.
Insignificant cancers were diagnosed by PSA in four cases, bpMRI with score 3-5 in seven cases; bpMRI with score 4-5 in five cases, ultrasonography with score 3-5 in 13 cases; and ultrasonography with score 4-5 in seven cases.
“This study suggests that when screening the general population for prostate cancer, MRI using a score of 4 or 5 to define a positive test result, compared with PSA testing alone at a level of 3ng/ mL or higher, might lead to more men being diagnosed with clinically significant cancer, without increasing the number of men advised to undergo biopsy or over diagnosed with clinically insignificant cancer,” write the authors.
One of the advantages of bpMRI, adds Eldred Evans, is that the technology is good at visualising aggressive cancers which are likely to shorten life, without diagnosing smaller ‘insignificant’ prostate cancers which are non-aggressive and commonly occur in men 60 years and over.
In an editorial accompanying the study, Susanna Lee and Aileen O’Shea, from Massachusetts General Hospital, write, “The IP1-PROSTAGRAM study lays the groundwork for future trials to examine the role of imaging in population-based prostate cancer screening.”
If MRI is to be developed as a screening tool, they add, additional future trials should be designed to include MRI in the prostate cancer screening strategy with image acquisition and interpretation protocols that are widely accessible, well tolerated and readily generalizable. “In the long run, if successful, prostate MRI will be able to join mammography and low-dose CT of the thorax as an imaging screening test that saves lives and improves the general health of the population,” they add.
The Imperial College team are currently raising funds for a more extensive screening trial to include 20,000 men. “We need to undertake much larger studies to confirm these results. If we achieve similar results we need to consider the practical implications of how MRI could be used on a larger scale. You could foresee an infrastructure, like breast cancer screening, where screening is offered in supermarket car parks and football stadiums,” says Eldred-Evans.