Posts by author
Janet Fricker
Advocates call for action to tackle damaging delays in myeloma diagnosis
Over one-third of European myeloma patients experience delays in diagnosis. ‘Myeloma Diagnosis Across Europe’, a pan-European survey and focus groups report published on European Myeloma Day (September 27th), revealed a landscape where diagnosis of myeloma can take over five months,…
Hope on horizon for blood test detecting unscreenable cancers
Multi-cancer early detection (MCED) tests offer a feasible approach for detecting 36 different types of cancer, over two thirds of which have no screening tests available. The PATHFINDER study, reported at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2022,…
NSCLC and climate change share common cause in particulate matter
Particles found in vehicle exhaust and combustion of fossil fuels are associated with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) risk. A study presented in the Presidential Symposium at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2022, held 9-13 September, showed increasing…
UK consensus group calls for biomarker testing at point of diagnosis
All cancer patients should be offered genomic profiling of their tumours at the point of diagnosis and during treatment to shape care and track how their disease evolves and responds to treatment. These were the conclusions of a UK consensus…
Frequent aspirin use associated with ovarian cancer risk-reduction
Frequent aspirin (acetyl salicyclic acid) use is associated with lower ovarian cancer risk regardless of the presence of most ovarian cancer risk factors. The meta-analysis of data from two ovarian cancer consortia, published in Journal of Clinical Oncology, 22 July,…
Resistant starch equivalent to eating a daily banana cuts hereditary cancer risk
Consuming resistant starch (RS), also known as fermentable fibre, reduces the risk of non-colorectal cancers (non-CRCs) by nearly 50% in people with Lynch syndrome. The study, published in Cancer Prevention Research, 25 July, found that while resistant starch significantly reduced…
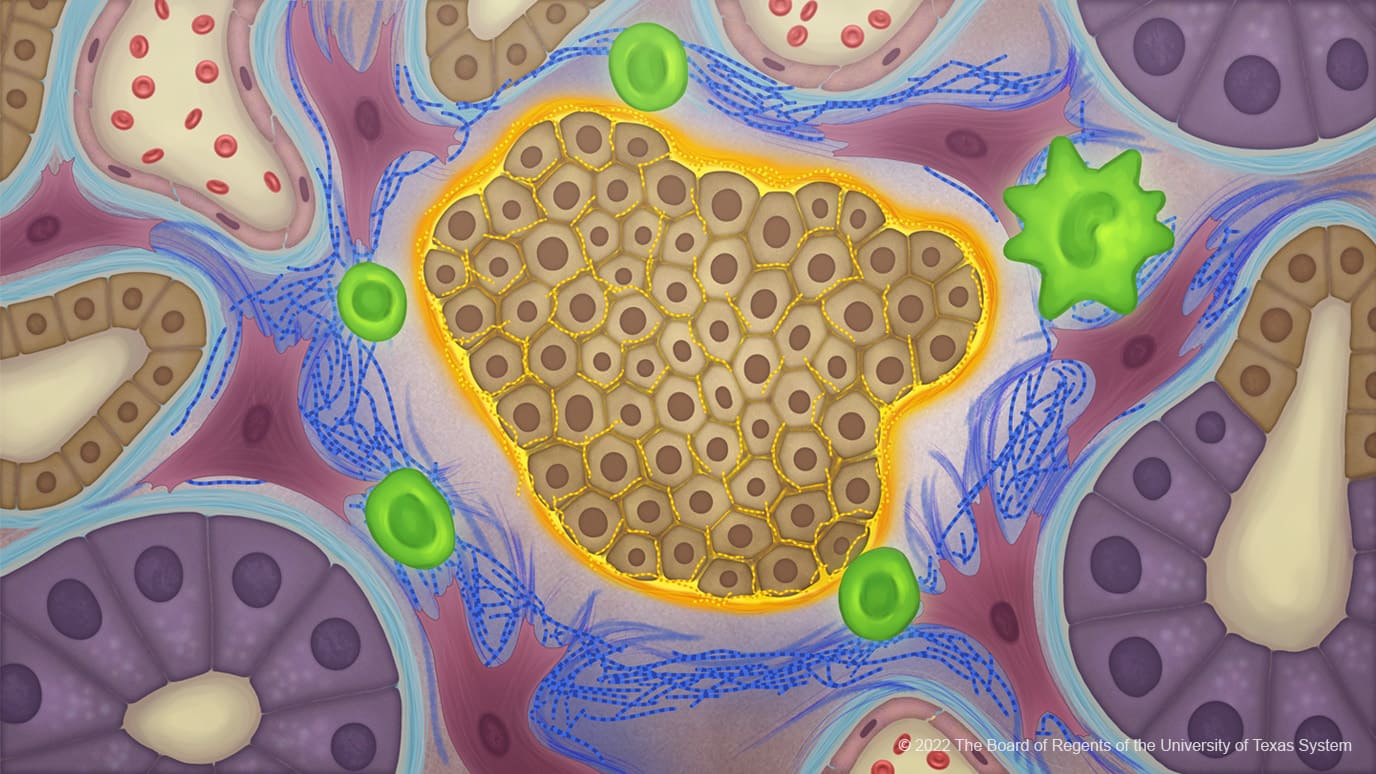
Abnormal collagen provides ‘invisibility cloak’ in pancreatic cancer offering new therapeutic targets
Cancer cells produce an atypical collagen in pancreatic cancer creating an extracellular matrix that influences the tumour microbiome to protect against immune responses. The study, published in Cancer Cell, July 21, suggests that such abnormal collagen could provide a new…
Study paves way for better checkpoint inhibitor response prognostication
Use of whole exome sequencing improves prediction of response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). The study, published in Nature Communications, 8 July, shows incorporation of the CIRCLE tool, including new genes and pathways identified from whole exome sequencing, leads to…
Pancreatic cancer patients diagnosed early through screening achieve long-term survival
The majority of high-risk patients diagnosed with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) while enrolled in a screening programme have stage I disease and can achieve long-term survival. The study, published in Journal of Clinical Oncology (June 15), found that in the…
Study defines increased risk of cardiovascular disease among cancer survivors
Adult survivors of cancer have a 37% higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) than people without cancer. The study, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, July 5 issue, found cancer survivors had a 52% higher…